the heart is
1 Definitions
The heart is a muscle that pumps blood throughout the body. to remain healthy, the heart needs oxygen and other nutrients carried by the blood. This is obtained through the artery (blood vessel) coronary, which wraps the outside of the heart.
The heart is a hollow muscular organ located in the center of the chest. part right and left heart each has space upper (atrial collect blood and lower spaces (ventricles) are issued Blood. In order for blood to flow only in one direction, then the ventricle has a valves at the entrance and at the exit of the valve.
The heart is a hollow organ and has four chambers which lies between both lungs in the middle thoracic cavity.
The heart is a muscular organ, conical, hollow and with its base above and below the peak. Its apex (peak) sloping side left.
The heart is a hollow muscular organ located in the center of the chest. part right and left heart each has space upper (atrial collect blood and lower spaces (ventricles) are issued Blood. In order for blood to flow only in one direction, then the ventricle has a valves at the entrance and at the exit of the valve.
The heart (Latin cor) is a hollow, hollow, muscular organ that pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. The term cardiac means relating to the heart, from the Greek cardia for
heart. The heart is one organ that plays a role in the circulatory system Blood.
The heart is a hollow organ that has a blunt conical four space which lies between the two lungs in the middle of the thoracic cavity. two thirds of the heart lies to the left of the line midsternal. The heart is protected
mediastinum.
2 Anatomy
a. Size and Shape

rests on the diaphragm thoracis and located approximately 5 cm above the processus xiphoideus.
On the right edge is at the edge of the cranial cranial pars cartilaginis costa III dextra, 1 cm from the lateral edge of the sternum. At the right edge of the caudal is at cranial edge of pars cartilaginis costa dextra VI, 1 cm from the lateral edge of the sternum. The left edge is at the heart of the cranial edge of the caudal pars cartilaginis costa II in the left lateral edge of the sternum, located on the left bank of the caudal space
intercostalis 5, approximately 9 cm in the left linea medioclavicularis.
Membrane that encloses the heart called the pericardium which consists between the fibrous and serous layers, the cavity contains 50 cc pericardii serves as a lubricant so that there is no friction between the pericardium and epicardium. Epicardium is the outermost layer of the heart, the layer The next layer is the layer where the myocardium is the layer thickest. The last layer is a layer of endocardium. On the right and left are divided into two chambers. cavity chamber next up is called the atria and the two lower chambers are called the ventricle which has a role in pumping blood into the arteries.
b. Casings
Pericardium is a double-walled pockets which can be enlarged and shrink, wrap around the heart and great vessels. this pouch attached to the diaphragm, sternum, vertebrae and pleural wrap
lung. Consists of layers of fibrous and serous. Fibrous layer composed of fibers collagen that forms the connective tissue layer of the meeting to protect heart. Visceral layer of serous consists of (epicardium) close
surface of the heart, and the fibrous parietal pericardium lines the inside. Pericardium cavity is a potential space between the visceral membrane and parietal. Contains pericardial fluid secreted for the serous layer
membrane lubricate and reduce friction. The pericardium is a double-walled pockets which can be enlarged and shrink, wrap around the heart and great vessels. this pouch attached to the diaphragm, sternum and pleura that encloses the lungs. Inside there are two layers of the pericardium which is the fibrous outer layer and in the serous layer. Pericardial cavity is a potential space betweenvisceral and parietal membrane.
c. Heart wall
Consisting of three layers, namely:
Epicardium composed of a layer of mesothelial cells that are above connective tissue.
Myocardium is composed of cardiac muscle tissue that contracts for pumping blood. Myocardial thickness varies from one heart chamber to other space. Muscle fibers are arranged in bundles of spiral
lining the heart chambers.
Endocardium composed of a layer of endothelial tissue located above connective. This layer lining the heart, valves, and connect with a layer endothelial lining of blood vessels entering and left heart.
d. Signs - Signs Surface
Coronarius sulcus (atrioventricular) surround the heart between the atria and ventricle. Anterior and posterior interventricular sulcus marks the location of the septum interventrikuler that separates the left and right ventricles. According to other sources, mentions that the sign - a sign of the heart surface are:
Coronary sulcus (atrioventricular) surround the heart between the atria and ventricle.
Anterior and posterior interventricular sulcus, separates the right ventricle and ventrikrl left
e. Fibrous framework Heart
attachment of the muscle and heart valves. As with other sources stating that, order cardiac fibrous nodules composed of fibrocartilage at the top interventricular septum and connective tissue ring around the meeting
basic pulmonary trunk and the aorta.
f. Heart space
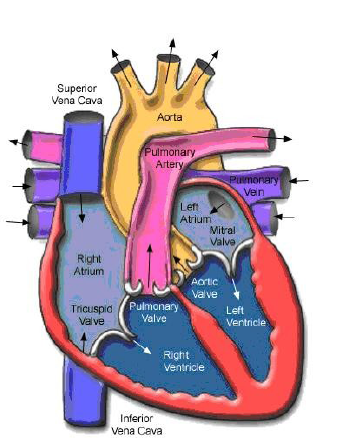
Atrium (separated by a septum intratrial) The right atrium is located in the superior portion of the right heart, receiving blood from all tissues except lung. Superior vena cava and Inferiorcarries blood from the heart to the entire body. Coronary Sinus bring return of blood from the heart itself wall. The left atrium in the superior portion of the left heart, smaller than the atrium Right, but the walls are thicker. Accommodates four pulmonary veins that returns oxygenated blood be lungs.
Ventricles (interventricular septum separated by) Located at the right ventricular apex of the heart in the right inferior. blood leave the right ventricle through the pulmonary truncus and flow passing a short distance to the lungs. Located at the inferior left ventricular apex of the heart on the left. thickness 3 times the wall thickness of the wall of the right ventricle. Blood left ventricular left through the aorta and flow throughout the body except the lungs. Trabeculae Carnae A muscular ridge round or irregular protruding from the inner surface of both ventricles to the ventricular cavity. Papillary muscles are trabeculae carnae protrusion attachment to place heart valve collagen cord (chorda tendinae). Moderator band (trabeculae septomarginal) is a curved band of muscle at right ventricle toward the transverse stretching of the septum anterior papillary muscle to the interventricular. This muscle helps in delivery transmission of impulses to the heart contraction.
There are four chambers, the right atrium and the left upper separated by a septum intratrial, bottom right and left ventricles are separated by a septum interventricular. Atrial walls are relatively thin. Atrium receives blood from the veinscarry blood back to the heart. The right atrium is located in the superior portion of the right heart, receiving blood from all tissues except the lungs. Superior and inferior vena cava brings blood that does not containoxygen from the body back to the heart. Coronary sinus blood brought back from the wall of the heart itself.Left atrium in the superior portion of the left heart, smaller than the right atrium, but the walls are thicker. Left atrium to accommodate four pulmonary vein returns oxygenated blood from the lungs.
Thick-walled ventricles. This section pushes blood out of the heart into the arteries that carry blood away from the heart. The right ventricle is located in the inferior part of the right at the apex of the heart. blood
leaving the right ventricle through the pulmonary trunk and flows passing a short distance to the lungs.
The left ventricle is located in the inferior part of the left apex of the heart. thickness walls 3 times thicker walls of blood leaving the right ventricle the left ventricle through the aorta and flow throughout the body except lungs. Trabeculae carneae is a relationship or irregular circular muscle that protruding from the inner surface of both ventricles to the cavity ventricular.
.
g. Heart Valve
tricuspid
Located between the right atrium and right ventricle. Has 3 valve leaflets (cusps) irregular fibrous connective tissue that is coated endocardium. The tip of the conical valve leaflets attached to chordae tendinae, which attached the papillary muscle. Chorda tendinae prevent reversal valve leaflets toward the back toward the atrium.
If the blood pressure in the right atrium is greater than the pressure towards left atrium, the tricuspid valve leaflets open and blood flows from atrium right ventricle to the right. If the blood pressure in the right ventricle is greater than the blood pressure diatrium right, leaves the valve will close and prevent backflow intoin the right atrium. Bicuspid (mitral) Located between the left atrium and left ventricle. This valve is attached to the Chorda tendineae and papillary muscles, the same function with the function of the tricuspid valve...
Aortic and pulmonary semilunar
Located in the heart ventricular exit lane to the aorta and truncus pulmonary. Pulmonary semilunar valve lies between the right ventricle and truncus pulmonary Aortic semilunar valve lies between the left ventricle and the aorta.Tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle. Bicuspid valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle. Aortic and pulmonary semilunar valve is located at the exit lane ventricular the heart to the aorta to the pulmonary trunk .
h. Blood flow to the heart
Pulmonary circuit is the path to go and leave the lungs. The right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body and flow into the lungs for oxygenated. Blood that has been oxygenated back to the left side of the heart. The right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle semilunar valves arteries
right and left pulmonary vein pulmonary capillary pulmonary left atrium. Systemic circuit is the path to and leaving the body. side left heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and drain into the whole body.
Left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle aortic semilunar trunk regia and organs of the body (muscle, kidney, brain)
i. Heart Induction System Components
Activity contraction of the heart to pump blood throughout the body always preceded by electrical activity. Inidimulai electrical activity on nodesinoatrial (SA node) located in the gap between the vena cava suiperior
and right atrium. In the SA node spontaneously initiated a wave of depolarization that cause action potentials propagated through the muscle cells atrial, atrioventricular node (AV node), the bundle of His, Purkinje fibers and eventually to the entire ventricular muscle....
Therefore, the heart never breaks to contract in order meet the needs of the body, the heart needs more
blood compared with other organs. Blood flow to the heart is obtained of the right and left coronary arteries. Both coronary arteries is out of the aorta approximately ½ inch above the running surface of the aortic valve and pericardium.
Then branching into arterioles and capillaries into the ventricular wall. After an exchange of O2 and CO2 in the capillary, venous outflow from ventricle was taken through the coronary veins and straight into the right atrium where the flow of venous blood from the entire body will lead. Blood circulation in your body there are 2 of the pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation. Pulmonary circulation from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery, a large artery and small, then go into the lung capillaries, after exit from the lungs through the venous small, and eventually pulmonary venous return to the left atrium. this circulation
have a low pressure of approximately 15-20 mmHg in arterial pulmonary. Systemic circulation starts from the left ventricle to the aorta and large arteries, the arteries small arterioles throughout the body and then to the venules, small veins, large veins, inferior vena cava, superior vena cava to the right atrium finally back.
Systemic circulation has a special function as a source of pressure tinggindan carry oxygen to tissues in need. on capillary terjadin O2 and CO2 exchange in which the systemic circulation O2 exit and CO2 into the capillary while the O2 entering the pulmonary circulation and CO2 out of the capillary. The volume of blood in circulation each component is different. 84% of the blood volume in the body found in the systemic circulation, where 64% the veins, arteries and 13% at 7% in arterioles and capillaries.
1). sinoatrial
2). atrioventricular
3). RA, LA, RV, LV


0 comments:
Post a Comment